System Architecture Overview
Architectural Diagram
A detailed diagram (see Appendix A) illustrates the interplay between front-end clients, the backend server, hybrid inference engines, quality verification modules, blockchain-based token management, external integration services, and the memory sharing protocol.
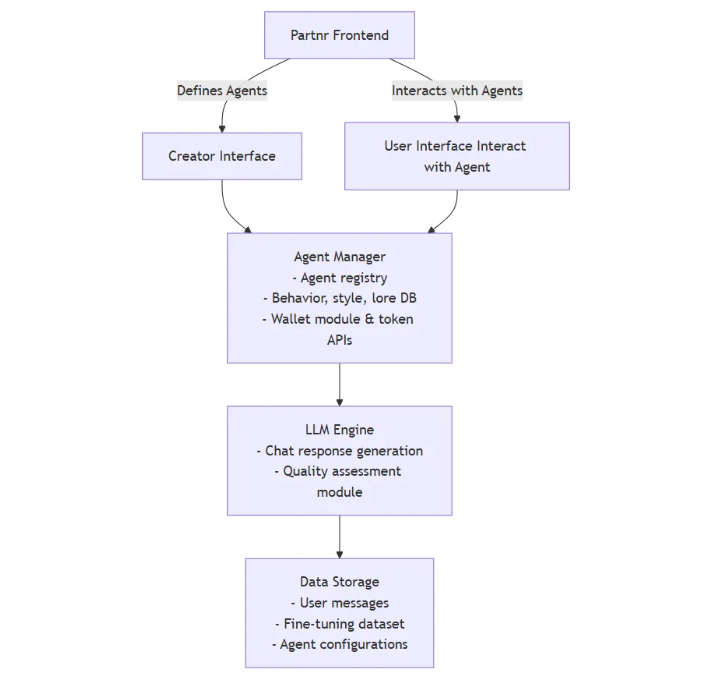
Components
Frontend
Creator Interface: Allows configuration, creation, and management of Agents (setting their lore, style, domain knowledge, etc.).
User Interface: Used by general users to chat with Agents and view rewards.
Agent Manager
Responsibilities:
Maintains the registry of all Agents and their configurations.
Handles agent-specific business logic, such as conversation routing and state management.
Interfaces with the LLM Engine to pass context and receive responses.
Architecture:
Stateless microservice deployed in containers, scalable horizontally.
Uses a relational database or document store for persistence of Agent configurations.
LLM Engine
Responsibilities:
Generates chat responses based on incoming user messages and Agent context.
Evaluates user messages for quality using custom scoring metrics.
Supports real-time interactions and asynchronous batch processing for fine-tuning data.
Architecture:
Deployed on GPU-enabled servers or specialized hardware accelerators.
Uses container orchestration (e.g., Kubernetes) to scale based on demand.
Modular design to allow plugging in alternative models (e.g., GPT-J, LLaMA, custom fine-tuned models).
Data Storage
User Messages: Captures conversation history and annotations (quality evaluations).
Fine-tuning Dataset: Periodically aggregated from flagged high-quality interactions.
Agent Configuration: Stores the lore, style, and custom logic associated with each Agent.
Databases: SQL (PostgreSQL, MySQL) or NoSQL (MongoDB) to store Agent configurations, user messages, and reward transactions.
Wallet & Token Module
Responsibilities:
Manages Agent wallets, token minting, token transfers, and internal ledger.
Interfaces with blockchain networks (if required) or an internal ledger system.
Provides APIs to trigger token rewards based on quality assessments.
Architecture:
Microservice with dedicated security measures, including encrypted key storage.
Supports smart contract integration for blockchain-based tokens.